CSS 盒模型
基本概念
标准模型
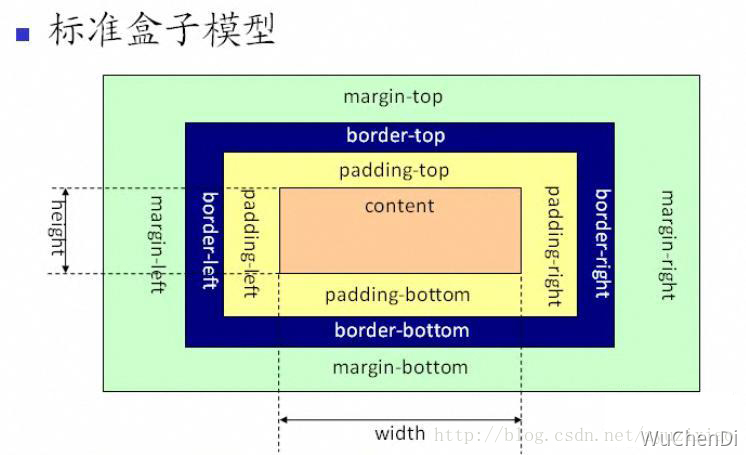 从上图可以看到标准 W3C 盒子模型的范围包括 margin、border、padding、content,并且 content 部分不包含其他部分。
从上图可以看到标准 W3C 盒子模型的范围包括 margin、border、padding、content,并且 content 部分不包含其他部分。
IE 模型
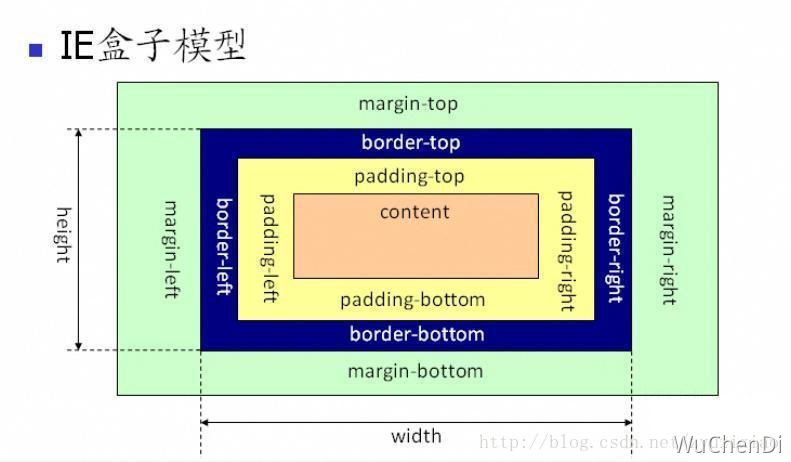 从上图可以看到 IE 盒子模型的范围也包括 margin、border、padding、content,和标准 W3C 盒子模型不同的是:IE 盒子模型的 content 部分包含了 border 和 pading。
从上图可以看到 IE 盒子模型的范围也包括 margin、border、padding、content,和标准 W3C 盒子模型不同的是:IE 盒子模型的 content 部分包含了 border 和 pading。
CSS 如何设置这两种模型
<!-- 标准模型 -->
box-sizing:conent-box;
<!-- IE盒模型 -->
box-sizing:border-box;
浏览器默认方式为:box-sizing:conent-boxJS 如何设置获取盒子模型对应的宽和高
dom.style.width / height
dom.currentStyle.width / height(ie支持)
window.getComputedStyle(dom).width / height
dom.getBoundingClientRect().width / height实例题(根据盒模型解释边距重叠)
 如上图:有两个元素其中子元素高度为 100px,子元素与父元素的上边距为 10px,求父元素的实际高度? 答案: 说 100px 对,说 110 也对,为什么捏?这个要看父元素的盒模型要怎么设置的
如上图:有两个元素其中子元素高度为 100px,子元素与父元素的上边距为 10px,求父元素的实际高度? 答案: 说 100px 对,说 110 也对,为什么捏?这个要看父元素的盒模型要怎么设置的
<style>
html,
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
#sec {
background: #f00;
}
.child {
height: 100px;
margin-top: 10px;
background: yellow;
}
</style>
<body>
<section id="sec">
<article class="child"></article>
</section>
</body>运行效果:
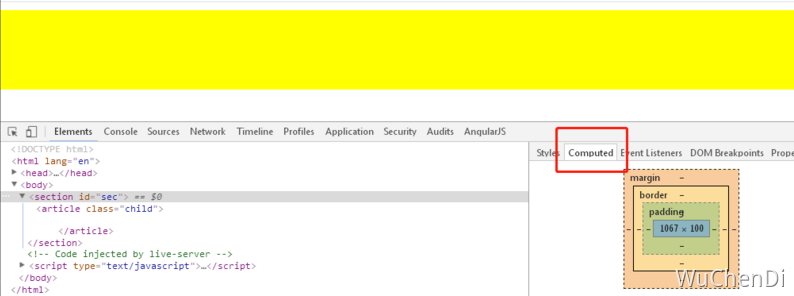 上图证明 100px 是对的 元素加个 overflow:hidden
上图证明 100px 是对的 元素加个 overflow:hidden
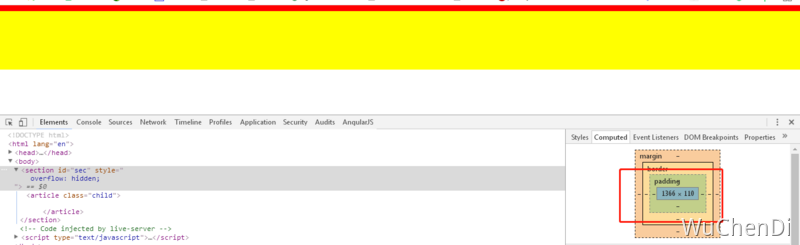 你会发现这时高度为 110px, 这时大家可能会疑问,为什么给父级元素设置一个 overflow:hidden 以后,它的高度就成 110 呢,这块的基本原理是啥呢,咋就这样呢?说这个之前,先引用一个知识点: 上面代码是父子元素边距重叠,那么还有两种情况边距重叠就是,一种是兄弟元素,就是两个 div 挨着,每个都上边距或者下边距,那么重叠的原则就是取最大值。 来回答上面问题:给父级加了 overflow:hidden,其实就是给父级元素创建一个 BFC(块级格式化上下文)。
你会发现这时高度为 110px, 这时大家可能会疑问,为什么给父级元素设置一个 overflow:hidden 以后,它的高度就成 110 呢,这块的基本原理是啥呢,咋就这样呢?说这个之前,先引用一个知识点: 上面代码是父子元素边距重叠,那么还有两种情况边距重叠就是,一种是兄弟元素,就是两个 div 挨着,每个都上边距或者下边距,那么重叠的原则就是取最大值。 来回答上面问题:给父级加了 overflow:hidden,其实就是给父级元素创建一个 BFC(块级格式化上下文)。
BFC
基本概念
Block Formatting Context, 块级格式化上下文,一个独立的块级渲染区域,该区域拥有一套渲染规格来约束块级盒子的布局,且与区域外部无关。
BFC 的原理
- BFC 这个元素的垂直的边距会发生重叠
- BFC 的区域不会与浮动元素的 float 重叠
- 独立的容器,内外元素互不影响
- 计算 BFC 高度,浮动元素也参与计算
如何创建 BFC
- float 不为 none 的时候
- position 不为 static 或者 relative 的时候
- display 与 table 相关的时候
- overflow 为 auto, hidden 的时候
BFC 使用场景
- BFC 垂直方向边距重叠
<section id="margin">
<style>
#margin {
background: pink;
overflow: hidden;
}
#margin > p {
margin: 5px auto 25px;
background: red;
}
</style>
<p>1</p>
<div style="overflow:hidden">
<p>2</p>
</div>
<p>3</p>
</section>- BFC 不与 float 重叠
<section id="layout">
<style media="screen">
#layout {
background: red;
}
#layout .left {
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: pink;
}
#layout .right {
height: 110px;
background: #ccc;
overflow: auto;
}
</style>
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</section>- BFC 子元素即使是 float 也会参与计算
<section id="float">
<style media="screen">
#float {
background: red;
overflow: auto;
/*float: left;*/
}
#float .float {
float: left;
font-size: 30px;
}
</style>
<div class="float">我是浮动元素</div>
</section>link 标签和 import 标签的区别
link 属于 html 标签,而@import 是 css 提供的 页面被加载时,link 会同时被加载,而@import 引用的 css 会等到页面加载结束后加载。 link 是 html 标签,因此没有兼容性,而@import 只有 IE5 以上才能识别。 link 方式样式的权重高于@import 的。
选择器,优先级
id 选择器,class 选择器,标签选择器,伪元素选择器,伪类选择器等
同一元素引用了多个样式时,排在后面的样式属性的优先级高;
样式选择器的类型不同时,优先级顺序为:id 选择器 > class 选择器 > 标签选择器;
标签之间存在层级包含关系时,后代元素会继承祖先元素的样式。如果后代元素定义了与祖先元素相同的样式,则祖先元素的相同的样式属性会被覆盖。继承的样式的优先级比较低,至少比标签选择器的优先级低;
带有!important 标记的样式属性的优先级最高;
样式表的来源不同时,优先级顺序为:内联样式> 内部样式 > 外部样式 > 浏览器用户自定义样式 > 浏览器默认样式